This page includes advice from WHO on ways to protect yourself and prevent the spread of COVID-19. The downloadable infographics below provide guidance on general and specific topics related to the pandemic.
In recent years, there has been increasing acknowledgement of the important role mental health plays in achieving global development goals, as illustrated by the inclusion of mental health in the Sustainable Development Goals. Depression is one of the leading causes of disability. Suicide is the fourth leading cause of death among 15-29-year-olds. People with severe mental health conditions die prematurely – as much as two decades early – due to preventable physical conditions.


1. Let go of past and future thoughts: If you let your mind wander into the past, you may waste your energy on regrets. If you think too much about the future, worries can drain your energy
2. Accept the present Moment: Accept the present moment just as it is without judgment so you can use your energy to directly handle the circumstance at hand.
3. Meditate: Breathe deep into your belly and follow your breath all the way in and out. Notice your belly rise and fall. Notice the air passing through your nostrils. Expect your mind to wander and simply return your attention back to your breath
4. Get in touch with your senses: Notice the sounds around you, the temperature of your skin, and the scents in the air. Slow down to notice what’s going on around you in the moment.
A healthy diet is a foundation for health, well-being, optimal growth and development. It protects against all forms of malnutrition. Unhealthy diet is one of the leading risks for the global burden of disease, mainly for noncommunicable diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and cancer.
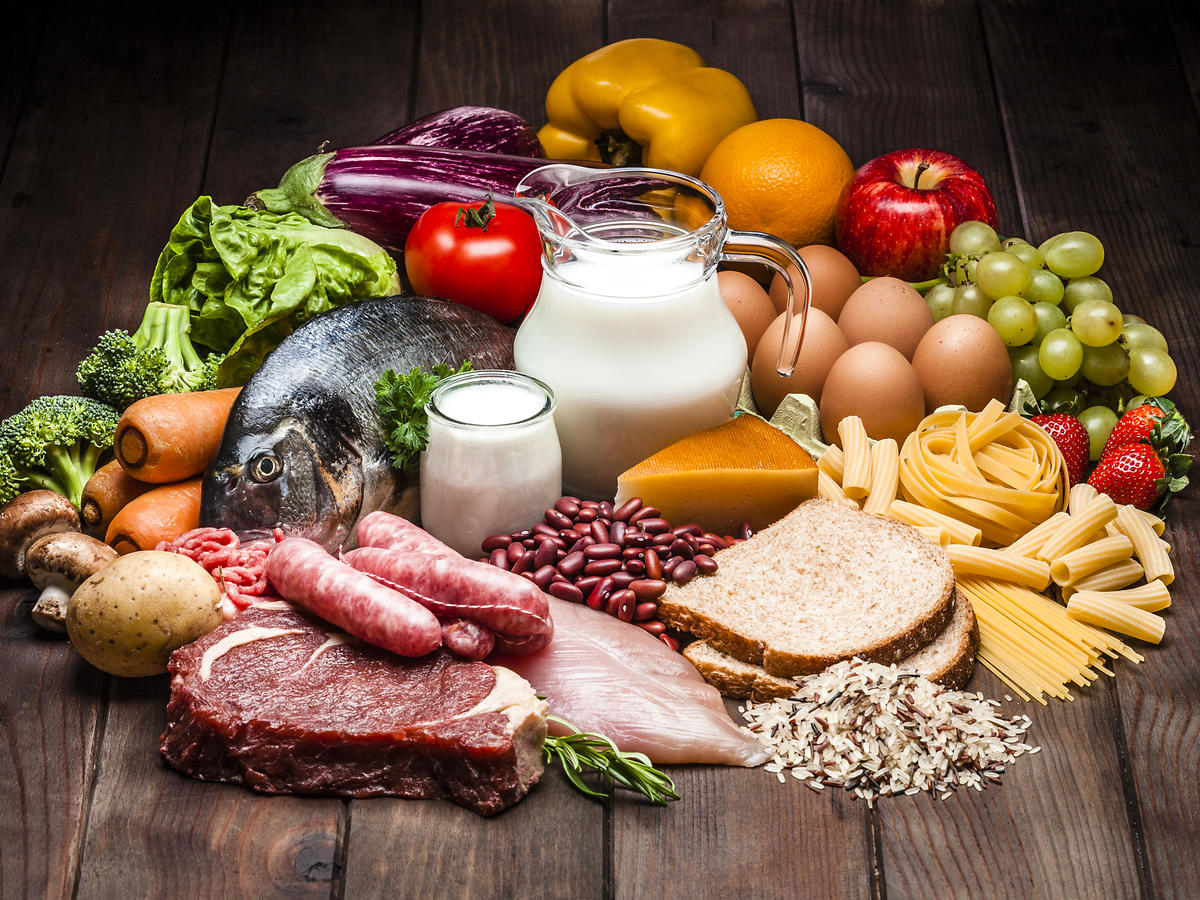


Evidence shows the health benefits of a diet high in whole grains, vegetables, fruit, legumes and nuts, and low in salt, free sugars and fats, particularly saturated and trans fats. A healthy diet starts early in life with adequate breastfeeding. The benefits of a healthy diet are reflected in higher educational outcomes, productivity and lifelong health.
A healthy diet is also more environmentally sustainable, as it is associated to lower greenhouse gas emissions, lower use freshwater and land mass.
Sexual health is fundamental to the overall health and well-being of individuals, couples and families, and to the social and economic development of communities and countries. Sexual health, when viewed affirmatively, requires a positive and respectful approach to sexuality and sexual relationships, as well as the possibility of having pleasurable and safe sexual experiences, free of coercion, discrimination and violence.
More than 30 different bacteria, viruses and parasites are known to be transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal and oral sex. Some STIs can also be transmitted from mother-to-child during pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding. Eight pathogens are linked to the greatest incidence of STIs. Of these, 4 are currently curable: syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis. The other 4 are incurable viral infections: hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus (HSV), HIV and human papillomavirus (HPV).
When used correctly and consistently, condoms offer one of the most effective methods of protection against STIs, including HIV. Although highly effective, condoms do not offer protection for STIs that cause extra-genital ulcers (i.e., syphilis or genital herpes). When possible, condoms should be used in all vaginal and anal sex.
STIs are often asymptomatic. When symptoms occur, they can be non-specific. Moreover, laboratory tests rely on blood, urine or anatomical samples. Three anatomical sites can carry at least one STI. These differences are modulated by sex and sexual risk. These differences can mean the diagnosis of STIs is often missed and individuals are frequently treated for 2 or more STIs

Ensuring access for all people to their preferred contraceptive methods advances several human rights including the right to life and liberty, freedom of opinion and expression and the right to work and education, as well as bringing significant health and other benefits. Use of contraception prevents pregnancy-related health risks for women, especially for adolescent girls, and when births are separated by less than two years, the infant mortality rate is 45% higher than it is when births are 2-3 years apart and 60% higher than it is when births are four or more years apart. It offers a range of potential non-health benefits that encompass expanded education opportunities and empowerment for women, and sustainable population growth and economic development for countries.
Road traffic crashes result in the deaths of approximately 1.3 million people around the world each year and leave between 20 and 50 million people with non-fatal injuries. More than half of all road traffic deaths and injuries involve vulnerable road users, such as pedestrians, cyclists and motorcyclists and their passengers.

Driving at speed significantly increases both the likelihood of a crash occurring, and the severity of its consequences. For every 1% increase in mean speed there is a 4% increase in fatal crash risk. The risk of death for pedestrians hit by motorized vehicles also rises rapidly as speed increases. A pedestrian hit by a vehicle travelling at 65 kilometres per hour is 4.5 times more likely to die than those hit by a vehicle travelling at 50 kilometres per hour.
Driving under the influence of alcohol or other psychoactive substances presents significant risk factor for road traffic injuries. In the case of drink driving, risk of road traffic injury increases significantly as the driver’s blood alcohol concentration goes up. In the case of drug-driving, the risk of road traffic injury increases to differing degrees depending on the psychoactive drug used.
Regular physical activity is proven to help prevent and manage noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes and several cancers. It also helps prevent hypertension, maintain healthy body weight and can improve mental health, quality of life and well-being. Physical activity refers to all movement. Popular ways to be active include walking, cycling, wheeling, sports, active recreation and play, and can be done at any level of skill and for enjoyment by everybody.

Regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, wheeling, doing sports or active recreation, provides significant benefits for health. Some physical activity is better than doing none. By becoming more active throughout the day in relatively simple ways, people can easily achieve the recommended activity levels.
In recent years, there has been increasing acknowledgement of the important role mental health plays in achieving global development goals, as illustrated by the inclusion of mental health in the Sustainable Development Goals. Depression is one of the leading causes of disability. Suicide is the fourth leading cause of death among 15-29-year-olds. People with severe mental health conditions die prematurely – as much as two decades early – due to preventable physical conditions.
The term “opioids” includes compounds that are extracted from the poppy seed as well as semisynthetic and synthetic compounds with similar properties that can interact with opioid receptors in the brain. Opioids have analgesic and sedative effects, and are commonly used for the management of pain. Opioid medicines such as methadone and buprenorphine are used for maintenance treatment of opioid dependence. After intake, opioids can cause euphoria, which is one of the main reasons why they are taken for non-medical reasons. Opioids include heroin, morphine, codeine, fentanyl, methadone, tramadol, and other similar substances. Due to their pharmacological effects, they can cause difficulties with breathing, and opioid overdose can lead to death.
Worldwide, about 500 000 deaths are attributable to drug use. More than 70% of these deaths are related to opioids, with more than 30% of those deaths caused by overdose. According to WHO estimates, approximately 115 000 people died of opioid overdose in 2017.


Nicotine contained in tobacco is highly addictive and tobacco use is a major risk factor for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, over 20 different types or subtypes of cancer, and many other debilitating health conditions. Every year, more than 8 million people die from tobacco use. Most tobacco-related deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries, which are often targets of intensive tobacco industry interference and marketing.
Electronic cigarettes (or e-cigarettes) are the most common form of electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) and electronic non-nicotine delivery systems (ENNDS) but there are others, such as e-cigars and e-pipes. ENDS contain varying amounts of nicotine and harmful emission.
The consumption of nicotine in children and adolescents has deleterious impacts on brain development, leading to long-term consequences for brain development and potentially leading to learning and anxiety disorders.